<Previous ………. Next Activity >
Construct a List & Matrix
Learn how …
- Activity 24 Presentation
- Activity 24 Practice
Do one on your own …
Details
Using the web article provided, make a meaningful list associated with the article. Make a list of six or more important points. Once completed, design a meaningful matrix based on the list.
Step-by-step Instructions
- Browse assigned web article.
- Break-down article into small subjects.
- Compile six or more small subjects.
- Make them into a list with smart headings.
- Design a matrix using list items.
- Make the matrix 2 columns x 3 rows or more.
- Give a meaningful title to the matrix.
Choose from …
- Physical Science articles
- Biology articles
- Earth Science articles
- Chemistry articles
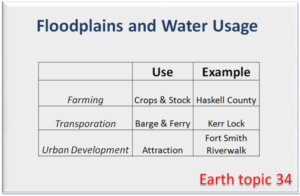
Example List & Example Matrix
General Instructions
The matrix should have a minimum of two columns and three rows. A meaningful heading (title) must be given to the matrix. Evaluate items from your list as a source for populating the cells in your matrix.
Time permitting, a two or three column numerical-based matrix might be designed – especially if the web article lends itself to doing so.
View these List Examples (pdf).
View these Matrix Examples (pdf).
Other Resources on this Site
Technique 15 – Creative Design
External Resources
2:40 Application of Matrices In Real Life
Standards for Activity
Science and engineering practices
This activity develops student skills in four of the eight science and engineering practices. Students identify, review, analyze information from a web article. Students create (develop) a matrix based on that information. Students communicate the information in the form of a graphical representation/summary of the information.
- Analyze and interpret data
- Develop and use models
- Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information
Cross-cutting Concepts
This activity supports student skills in three of the seven crosscutting concepts. Each matrix created by students has the potential to illustrate one or more of these concepts:
- Patterns *
- Systems and System Models *
- Structure and Function *